Defending the Blinds in Poker: Why It Matters?
In poker tournaments, the size of mandatory bets, known as blinds, continually increases. Meanwhile, opponents frequently attempt to steal them with raises from late positions. If you don't defend the blinds, your stack will start to diminish even without participating in the big hands.
It is important to understand: folding on the big blind in every hand means losing over a hundred big blinds over a hundred such hands, and on the small blind - more than fifty considering the ante. If you do not defend your blinds, you will never progress far in a tournament and will lose money.
The aim of defending blinds is not to play each individual hand profitably. Defending blinds is necessary to reduce inevitable losses. This way, you minimise your losses, resist blind theft, and maintain your stack over the long run.
Principles of Blind Defence
Defending blinds is a response to an opponent's raise when you are on the small or big blind. The basic idea is simple: do not allow the opponent to take your contribution to the pot without a fight.
However, defending blinds does not mean calling every raise. Proper defence is built on three key nuances:
Position
The position of the raiser at the table plays a key role. Players from late positions enter the game with a wider and weaker range of starting hands, whereas an early position raiser indicates a strong range. Accordingly, you should defend blinds against raises from early positions more cautiously.
Your own position is equally important. On the big blind, fewer chips are required to call, so you can call a raise with a broader range of hands compared to the small blind. Furthermore, when on the big blind, you close the preflop betting round and always know how the other players have acted.
On the small blind, the situation is different: there is still a player on the big blind to act behind you, creating additional uncertainty. Therefore, the small blind should be defended with a stronger range.
Size of the Raise
The smaller the size of the raise, the more frequently you can defend. If an opponent raises the standard size of 2 big blinds, you are offered favourable pot odds on the call with many hands that would not be played from free positions. Defence against larger raises should be narrower.
Type of Opponent
Different opponents play differently preflop and postflop. An active opponent will raise more frequently with a wider range of starting hands and play aggressively postflop, even without a good hand. A passive opponent attacks blinds much less often, usually with good starting hands, but often surrenders if they miss the flop. This should be taken into account.
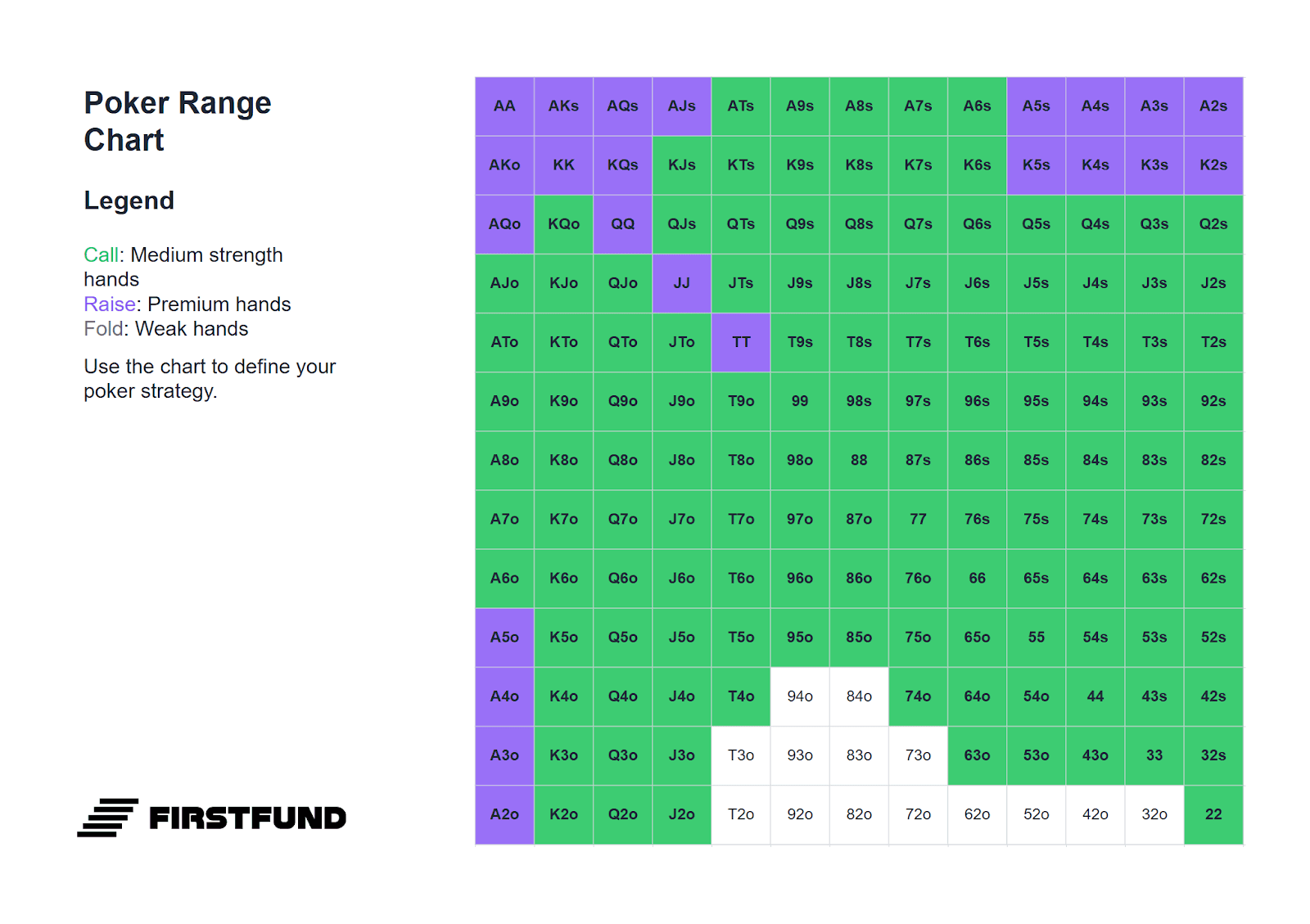
How to Defend the Big Blind?
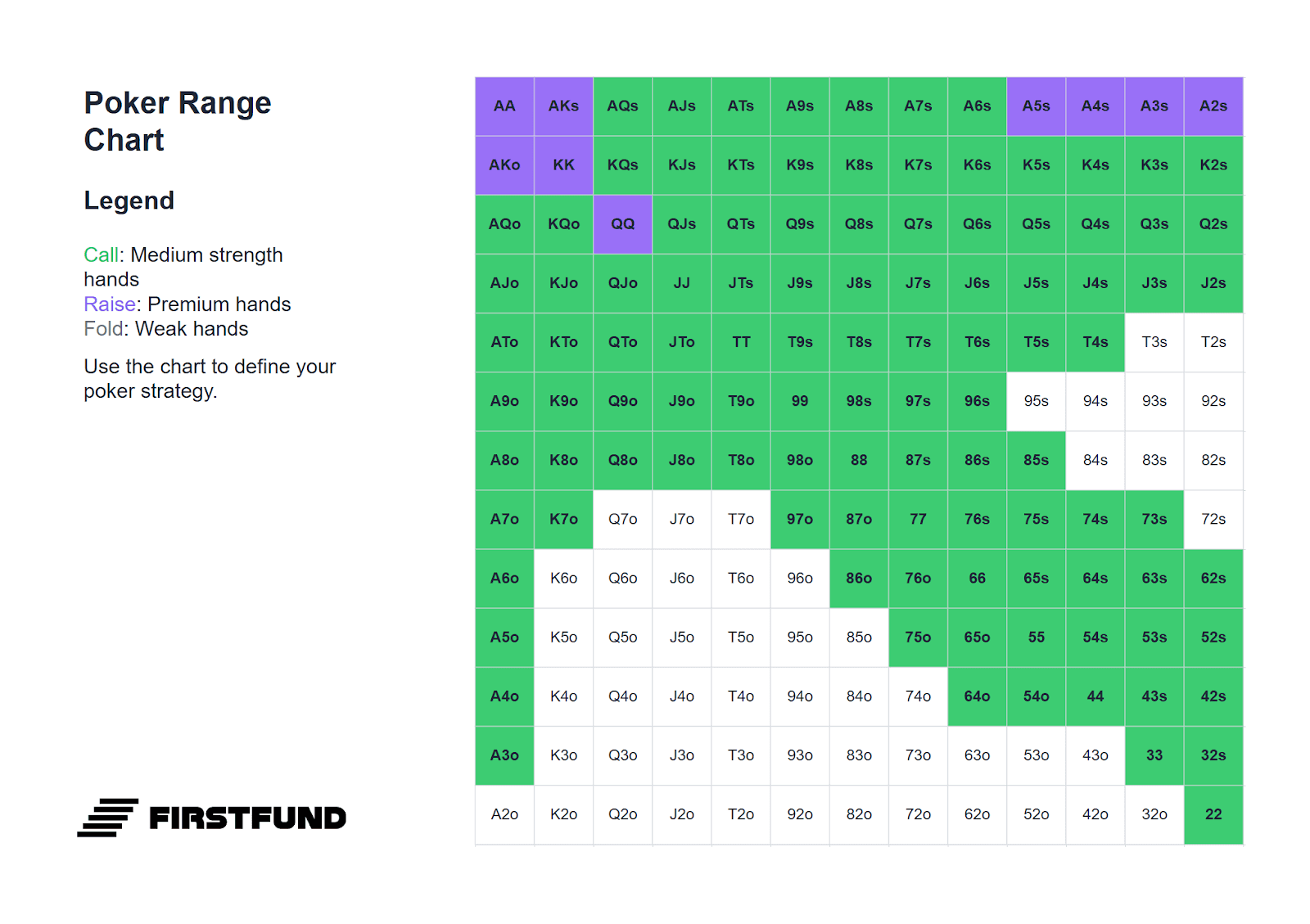
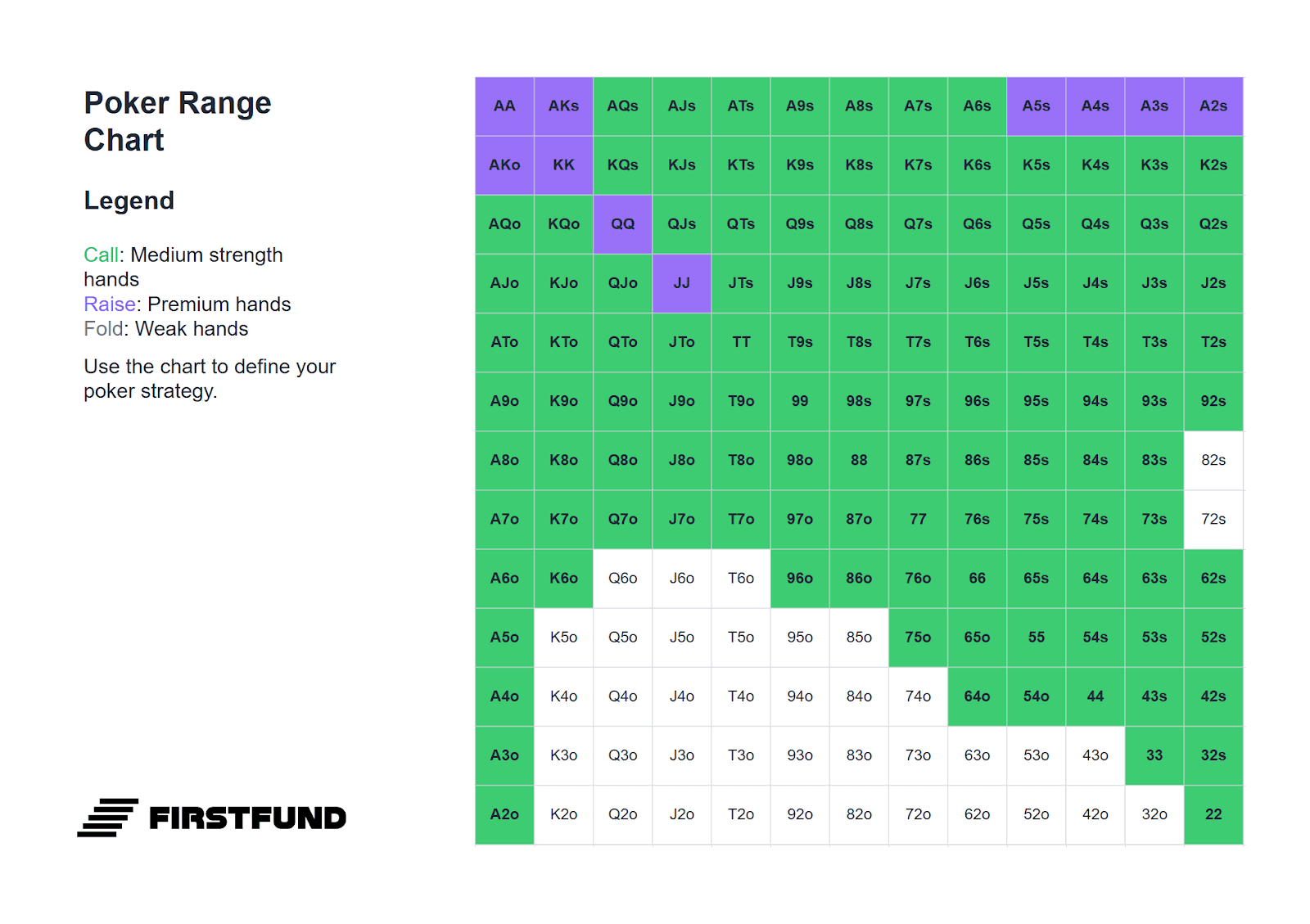
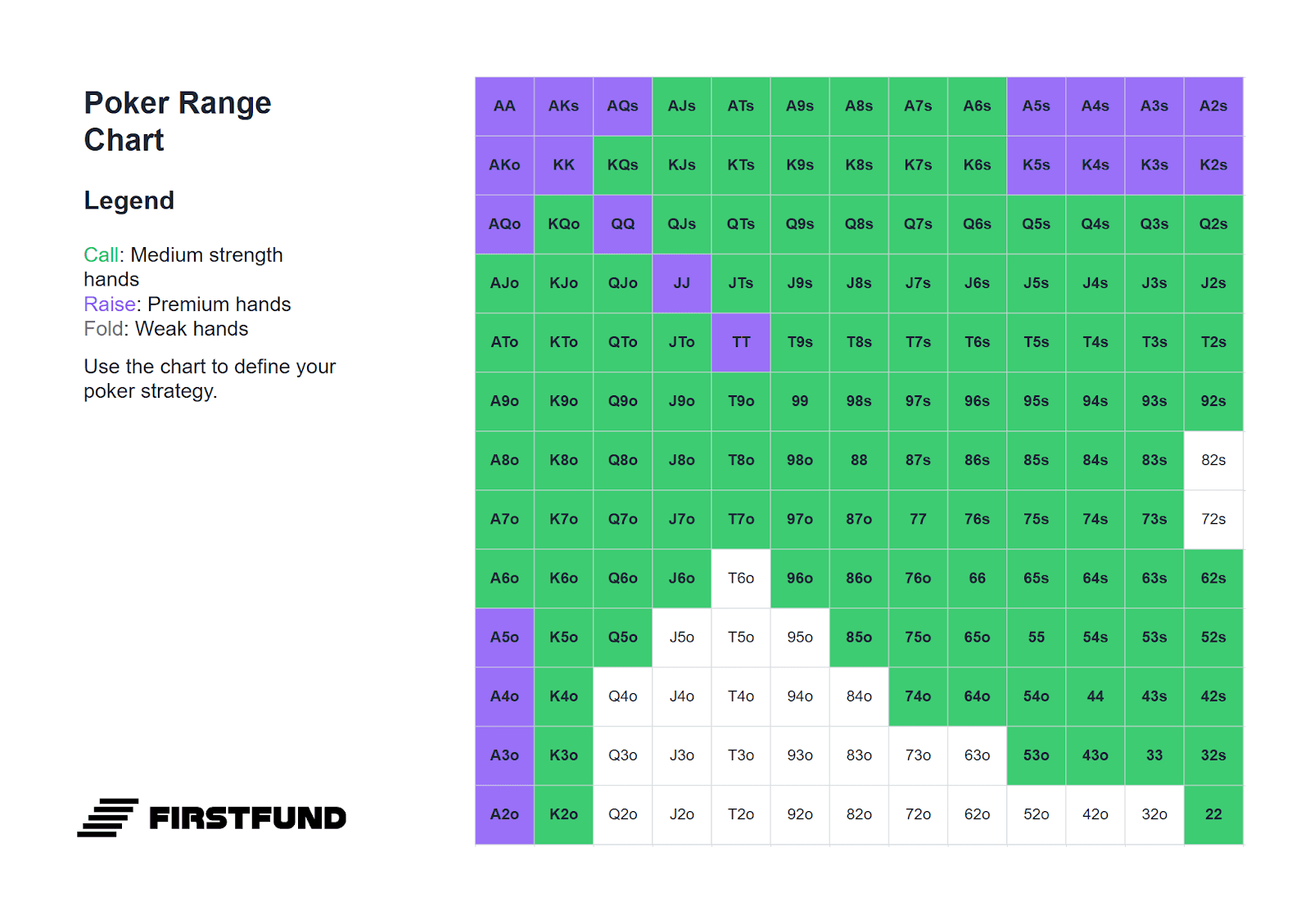
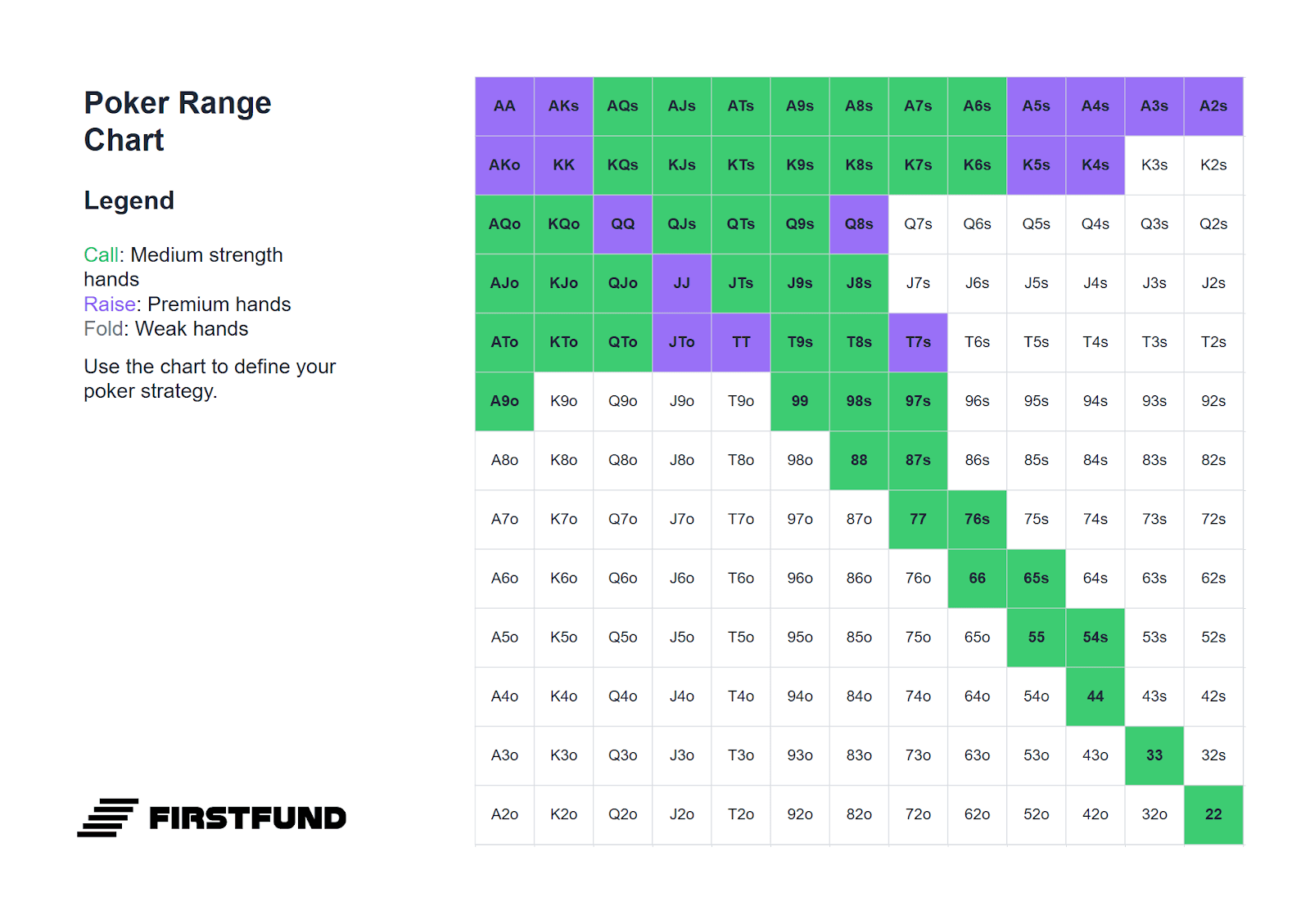
Below is a range of hands suitable for defending the big blind. It should be borne in mind that the choice of hand depends on the position of the player who made the raise: the earlier the raiser's position, the more cautious your range of defence should be.
All hands highlighted in green can be played by calling. Combinations highlighted in purple are suitable for playing either by calling or with a standard 3-bet: four times the size of the opening. For example, if an opponent makes a raise of 2 big blinds, the optimal 3-bet size would be 8 blinds.
If the size of the raise exceeds 2.5 big blinds, pay more attention: such raises often signal a strong hand. In such situations, your range of defence by calling and 3-betting must be narrower.
Against Early Position (EP)
Against Middle Position (MP)
Against Cutoff (CO)
Against Button (BTN)
How to Defend the Small Blind?
Below is a range of hands suitable for defending the small blind. It is significantly narrower than the range for defending from the big blind, because calling on the small blind requires adding one and a half big blinds, whereas on the big blind only one. Moreover, after your action, there is still one player remaining - the big blind. Their decision can alter the course of the hand, so overly wide defence from the small blind often leads to playing out of position in difficult postflop situations.
All hands highlighted in green can be played by calling. Hands highlighted in purple can be played either by calling or with a standard 3-bet: four times the size of the bet. If the raise size is greater than 2.5 big blinds, defend more narrowly - just as on the big blind, but with a narrower range.
Against Early Position (EP)
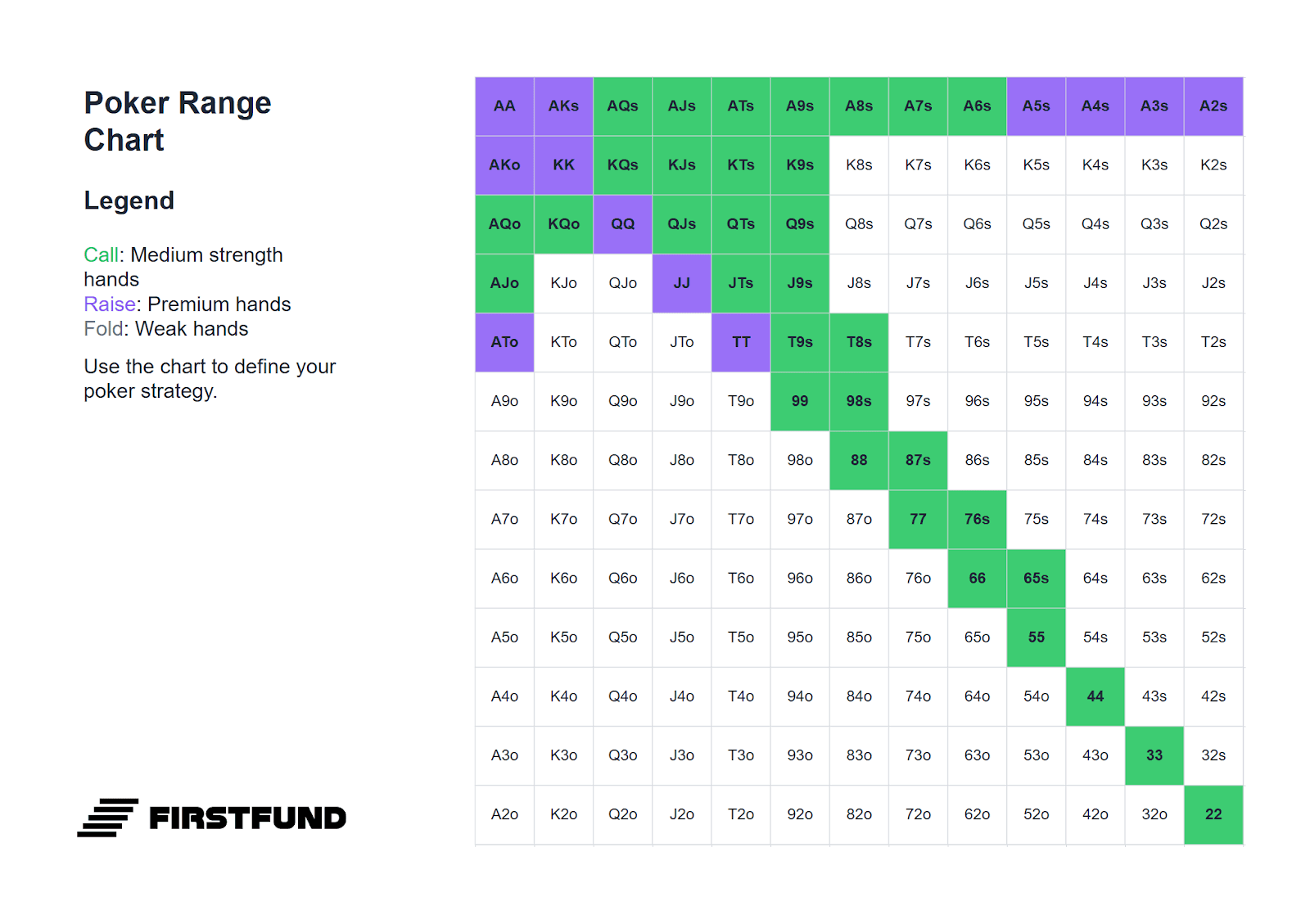
Against Middle Position (MP)
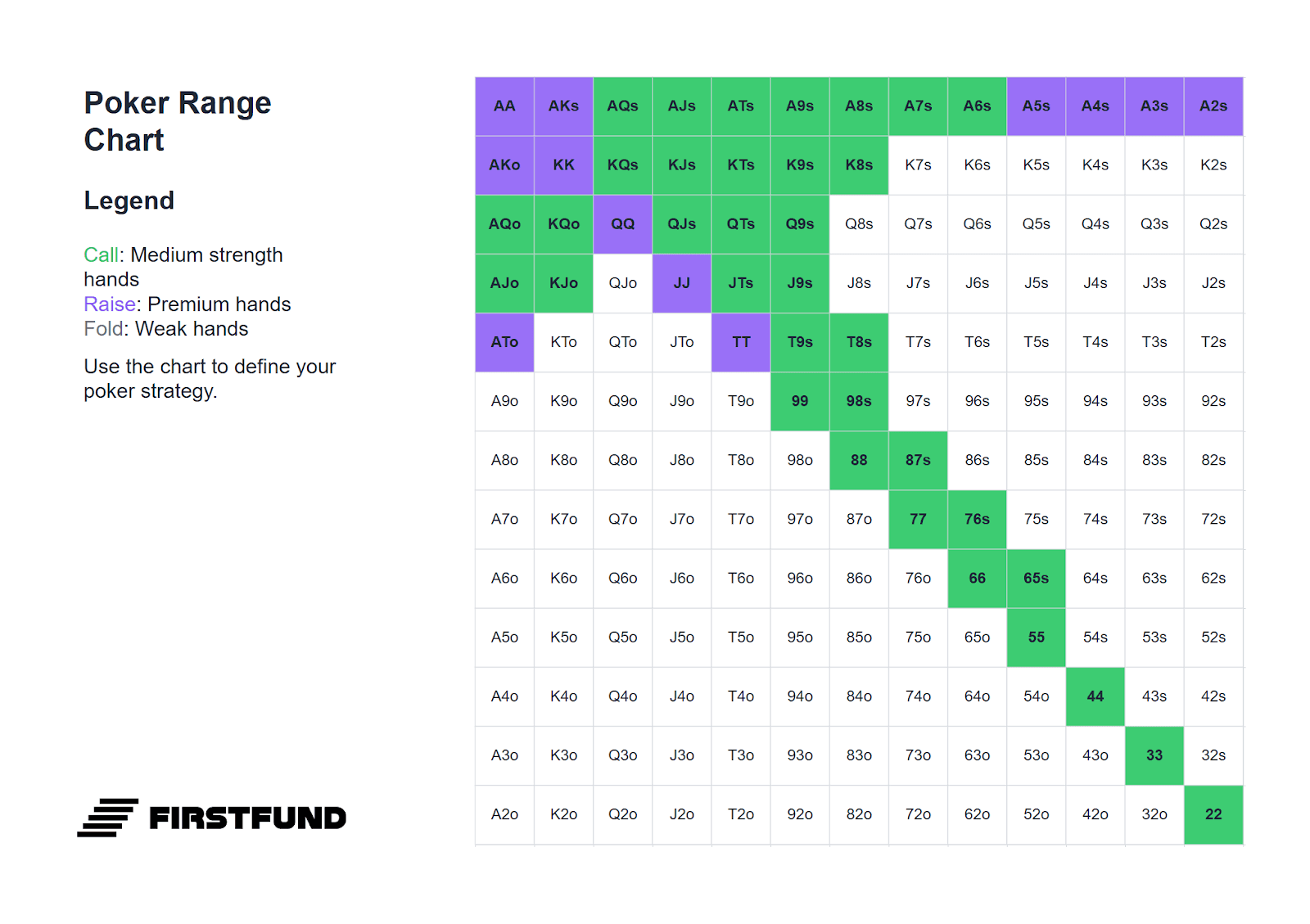
Against Cutoff (CO)
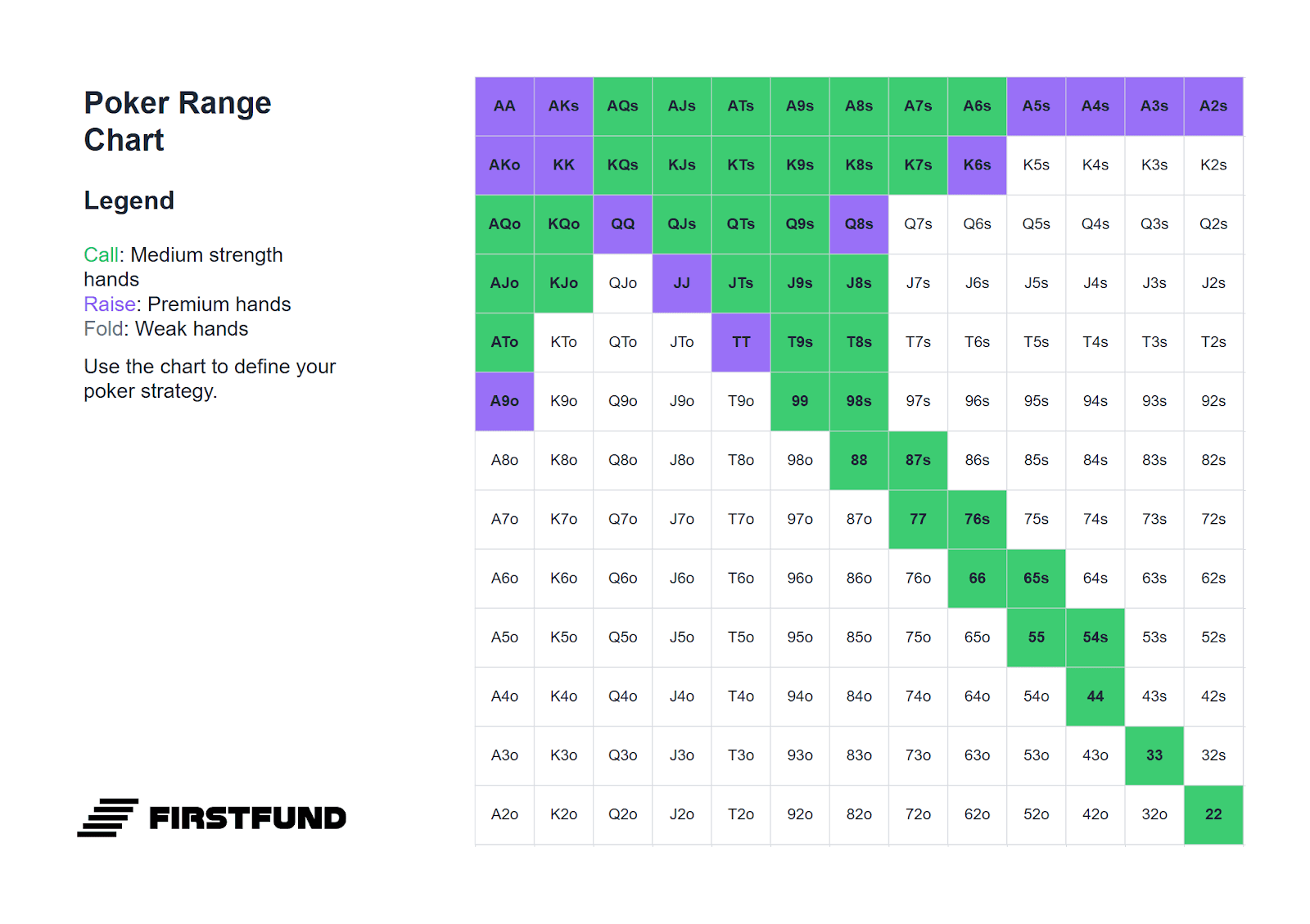
Against Button (BTN)
Conclusion
Proper blind defence is one of the key components of a profitable tournament strategy. A player who does not defend blinds inevitably loses a significant part of their stack, fails to go far in tournaments, and loses money.
When defending blinds, pay attention to the opponent's position, the size of their raise, and your own chances of improving your hand. Do not be afraid to call on the blinds with suitable hands: in the long run, a well-thought-out strategy in this position will allow you to maintain your stack at a stable level and not lose chips.
FAQ
Why is blind defence so crucial in tournaments?
Because the blinds steadily increase, and if you don't defend them, you'll lose your stack regardless of your play quality. This will inevitably lead to elimination from the tournament.
Should I aim to win the pot every time I defend a blind?
No. The aim of defence is not to win a specific hand, but to reduce inevitable losses. Fold easily if you miss the flop and focus on winning pots where you connect with the flop.
Why is the big blind defended more widely than the small blind?
On the big blind, you need to add fewer chips to call a raise, giving you more favorable pot odds. Additionally, you finish the preflop betting round and act last.
Why do you suggest playing 3-bets with hands that aren't the strongest?
If you only play good starting hands this way, opponents will quickly suss out your strategy. The defence range is balanced like this: play the best and the weakest hands through 3-bet, and the middle of the range through a call. This way, it's harder for your opponent to discern whether you're raising their bet with a strong hand or bluffing.